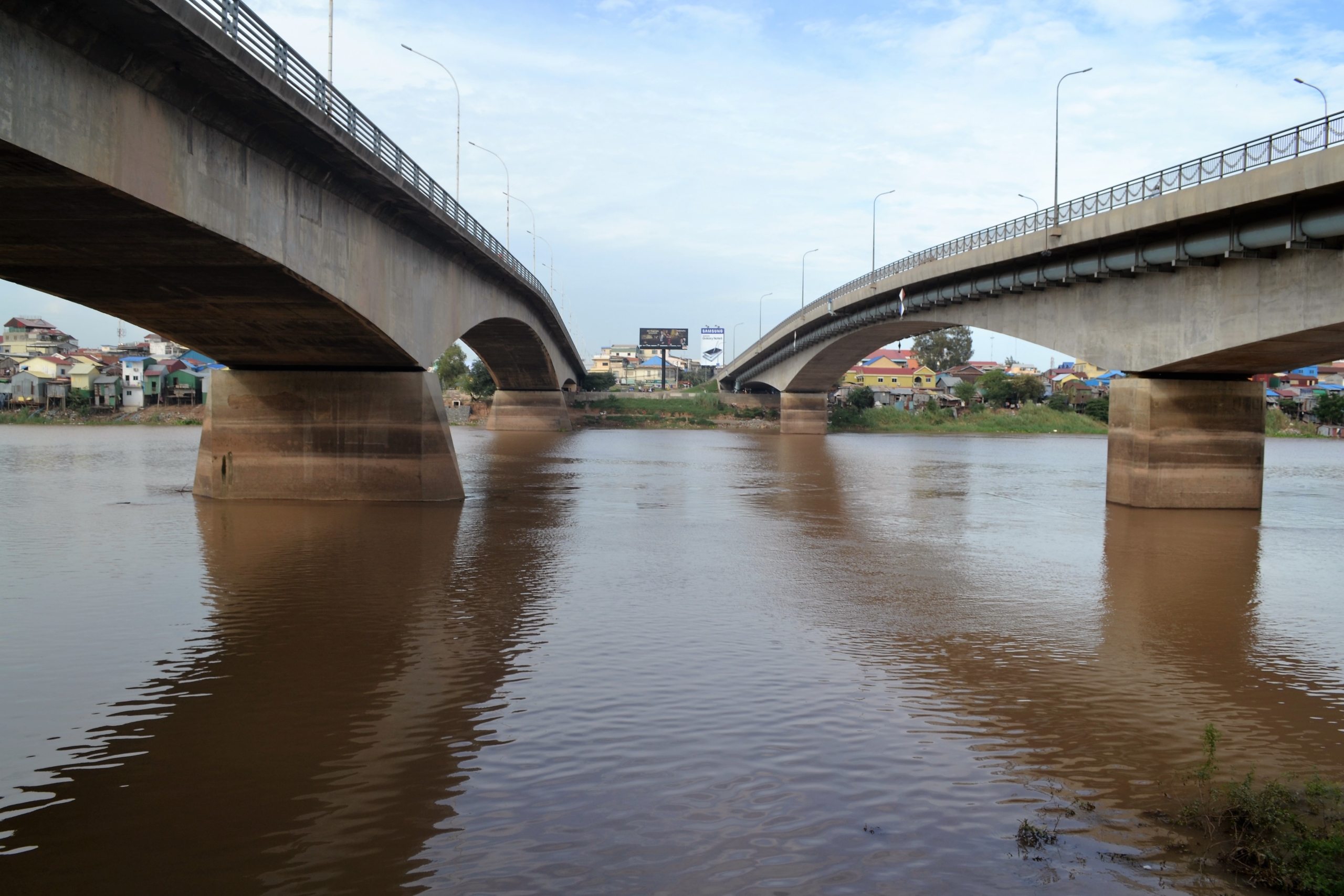
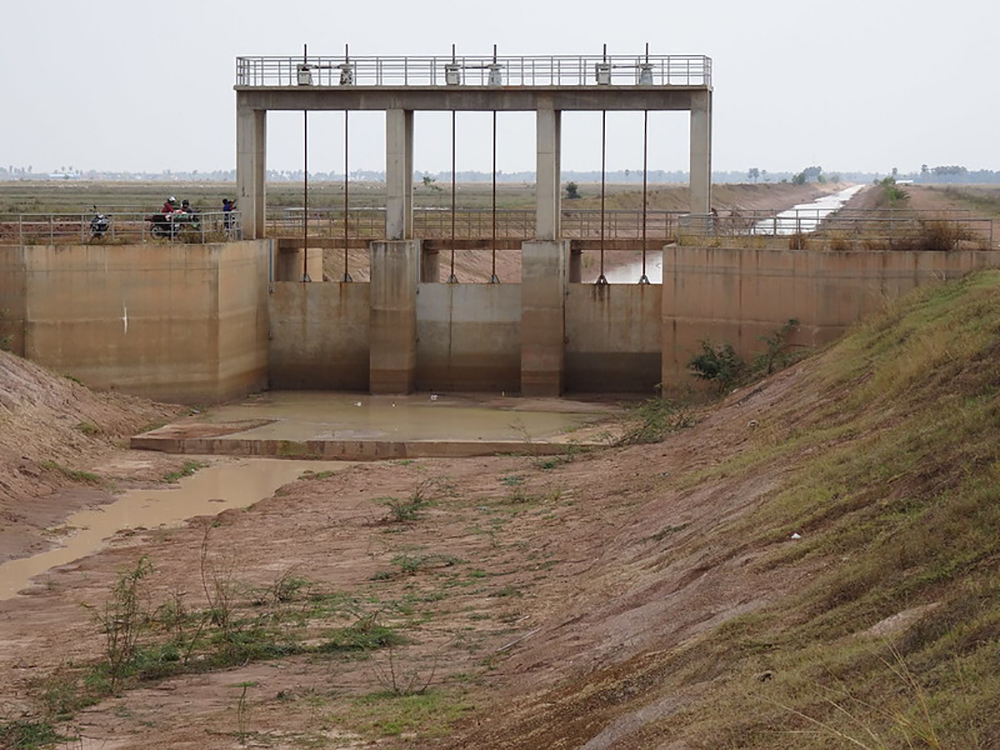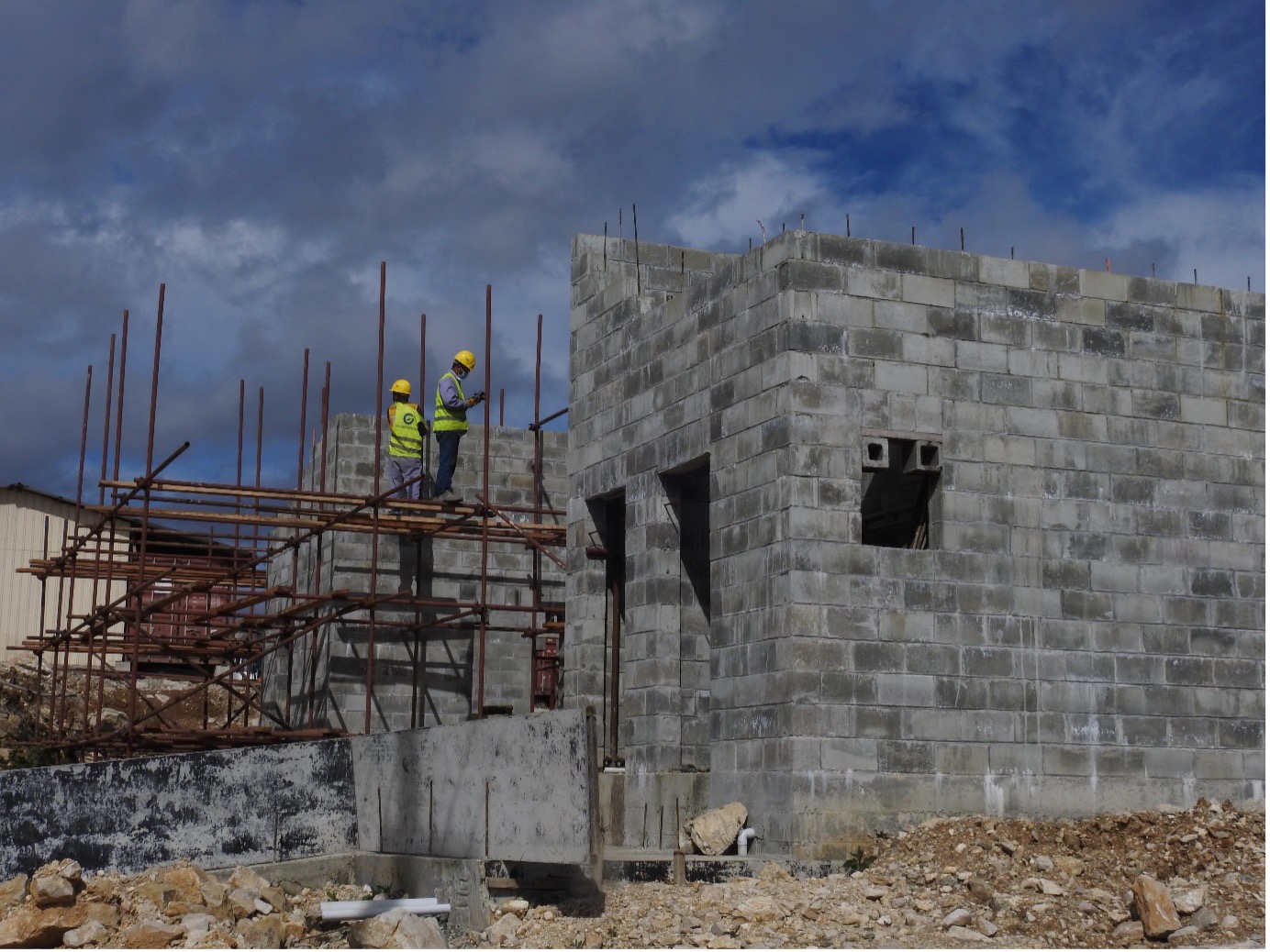

The National Road 1 (NR 1) Project was formulated in 2004 as part of a larger national development strategy to rehabilitate Cambodia’s roads and ports. It was fully funded by the Japanese International Cooperation Association (JICA), Japan’s leading foreign development agency. Although it began before the BRI was established, during a time when Cambodian state capacity was significantly weaker, Japan outperformed China in all areas.
Read More
The National Road 6 (NR 6) is a 415.5 km Cambodian highway stretching from the capital city of Phnom Penh to Banteay Meanchey Province in northwestern Cambodia on the border of Thailand. This major road connects both the cities of Phnom Penh and Siem Reap to the Thai border, designating it as a crucial international trade and transport corridor for the Kingdom. Investment in the road’s upkeep and maintenance is therefore essential, and the Royal Government of Cambodia (RGC) has welcomed overseas investment to this end. NR 6 is sectioned in line with its crossing of provincial borders and according to administrative authority. One such example is the Ang Krong-Thnal Kaeng (AKTK) section.
Read More
The Tatay River Hydropower Dam project is the sixth hydropower dam financed by China in Cambodia. The 246-megawatt Tatay River HydroPower dam is located in Thma-Bang District, Koh Kong Province in western Cambodia. The project is owned by Cambodian Tatay Hydropower Limited and began full operation in December 2015. When the Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) agreement for the project was signed in 2008, it was projected to start construction in 2009 and commence commercial operation by 2013 with a projected cost of $505 million. Upon the project’s inauguration, it was the largest investment project by a Chinese state enterprise in Cambodia to date.
Read More
The East Coast Rail Link (ECRL) is a proposed railway infrastructure project designed to improve connectivity between Peninsular Malaysia’s East Coast states of Kelantan, Terengganu, and Pahang, and the West Coast states of Negeri Sembilan, Selangor, and the Federal Territory of Putrajaya, which is currently only partially connected by rail. The railway will be used for both passenger and freight transportation. The journey from Kota Bharu, on the north end of the rail line, to Gombak, on the south end, will take less than four hours as compared to seven hours by car/bus. In addition to improved connectivity, the ECRL is intended to spur the development of the industrial, commercial, and tourism sectors along its route. A groundbreaking ceremony was held on August 9, 2017, to mark the start of construction. As of March 2021, 21.4 percent of the project had reportedly been completed. The rail line is scheduled to commence operation by 2027.
Read More
The Gemas–Johor Bahru Electrified Double-Tracking Project (G-JB) is a project to construct a double-track electric rail line from the town of Gemas in the state of Negeri Sembilan to the city of Johor Bahru in the state of Johor at the southern tip of Malaysia. It is the final component of the Malaysian Ministry of Transport’s broader electrified double-tracking project (EDTP); its completion will ensure a continuous double-track line across Malaysia from Padang Besar at the Thai border all the way to Johor Bahru, adjacent to Singapore.
Read More
The Melaka Gateway is a planned integrated seashore development project in the coastal areas of Melaka, a state at the southern tip of the Malaysian peninsula. It was conceptualised as a maritime centre that would host the largest private marina in Southeast Asia, reinstating Melaka’s reputation as a renowned trading zone while reviving the state’s economy. It is owned by a local developer, KAJ Development Berhad, with investments by three Chinese companies. In 2021, the project was cancelled indefinitely, and its land reclamation projects were rebranded as the Melaka Economic Waterfront Zone (M-WEZ). As of March 2022, however, the project has been handed back to KAJD and is back in development.
Read More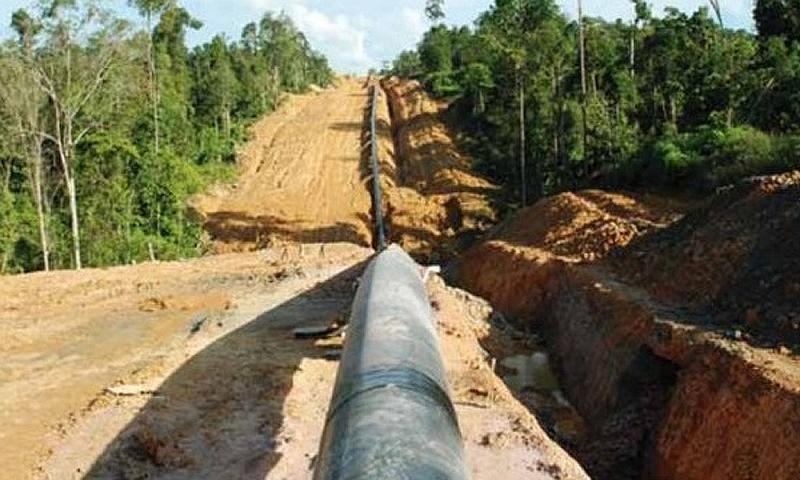
The Trans-Sabah Gas Pipeline (TSGP) is a RM4.06 billion (US $969.9 million) petrochemical and gas pipeline project that aims to provide a solution to the power shortage problem in Sabah, as well as increase job opportunities in the region and move Sabah higher up the value chain. It is commonly stated by media outlets, think tanks and academics that the TSGP is a BRI-related project, although this is not officially confirmed. The pipeline will be installed from the oil and gas terminal in Kimanis, Sabah to Sandakan and Tawau. The project owner is Suria Strategic Energy Resources Sdn Bhd (SSER), a special purpose vehicle established in 2016 to implement the project.
Read More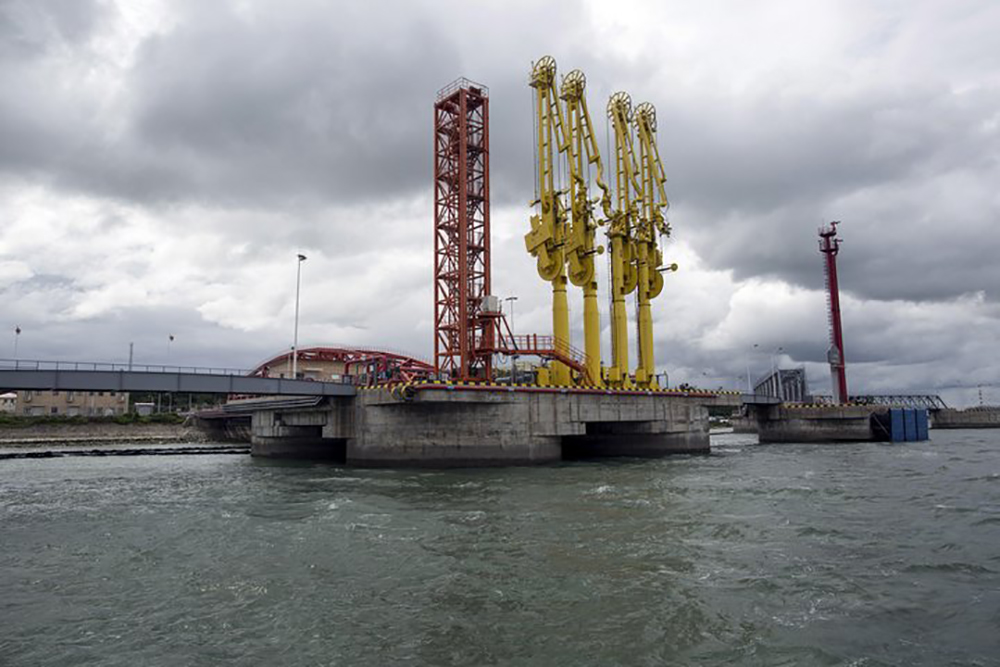
The Kyaukphyu Special Economic Zone (KP SEZ) is one of three special economic zones in development in Myanmar. Located on the Bay of Bengal in Kyaukphyu, Ramree Island, Rakhine State, it is planned to contain a deepwater port facility, an industrial zone, and a high-end housing project across a total of 4,300 acres. A primary goal of the special economic zone is to create employment opportunities for native Rakhine people in the area, using foreign direct investment to create jobs and generate tax revenues that will raise the local standard of living.
Read More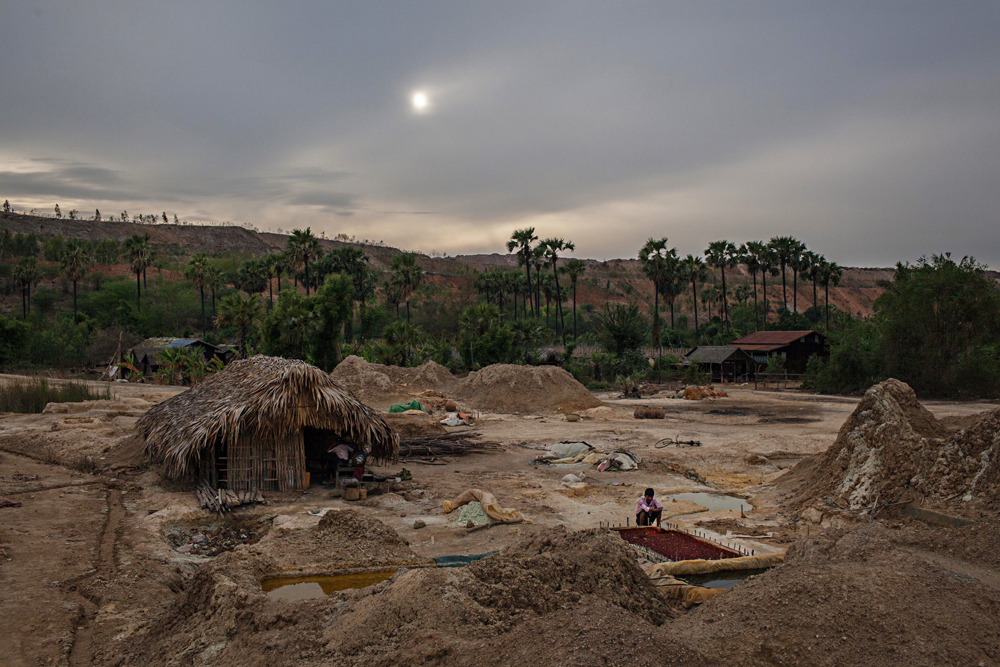
The Letpadaung Copper Mine Project is a Sino-Burmese joint venture project between Myanmar Wanbao Mining Company Ltd. (MWMCL), military-owned Myanmar Economic Holdings Ltd. (MEHL), and state-owned enterprise Mining Enterprise No. 1 (ME-1) of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Conservation (MoNREC). It aims to fulfill domestic raw materials for mineral resources and promote exports of the same which will encourage the growth of heavy industries, leading to long-term national development.
Read More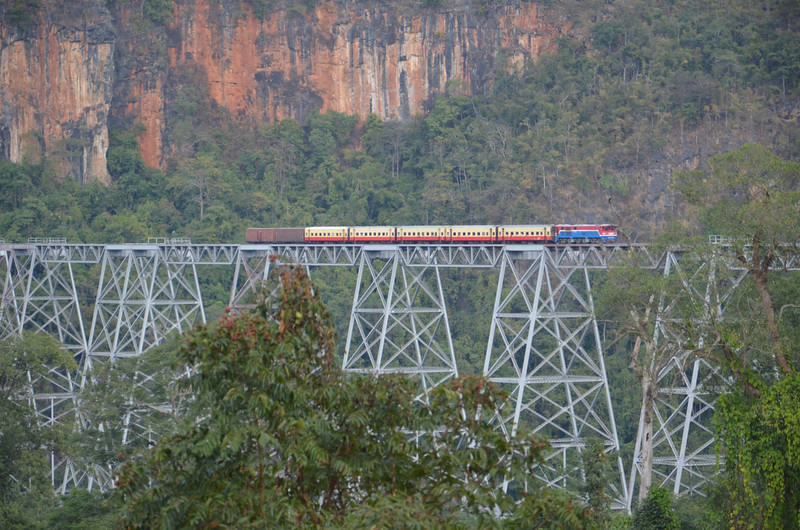
The Muse-Mandalay Railway project is a proposed 431-kilometre long standard-gauge railway project situated across the China-Myanmar border with an estimated cost of USD $9 billion. The railway is planned to connect Kunming, the capital of China’s southern Yunnan province, to Mandalay in central Myanmar. It represents a major part of the China-Myanmar Economic Corridor (CMEC). Official action began with the signing of a memorandum of understanding (MoU) in 2011 between China and Myanmar, but work on the Muse-Mandalay railway was suspended in 2014 due to strong objection from local people. The project was revived in 2018 during the National League of Democracy (NLD) government’s term. As of 2021, the Muse-Mandalay Railway project remains in the planning stages. However, it is expected that the military junta—the State Administration Council (SAC)—will approve the construction.
Read More
The Myanmar-China Oil and Gas Pipeline projects involve two Chinese-built and operated pipelines that transport natural gas and crude oil from Myanmar’s West Coast to China, extending into Yunnan Province. The pipelines were completed in 2013 and 2017, respectively, and began moving Myanmar’s natural gas as well as energy imports from the Middle East.
Read More
The Kumul Submarine Cable Network Project (KSCNP) is a project to establish a submarine optic cable of 5,475 kilometers linking fourteen coastal provinces within Papua New Guinea (PNG). It is the second component of the larger Coral Sea Cable Project which aims at increasing information sharing and strengthening existing bilateral relations between Australia and PNG.
Read More
The Pacific Maritime Industrial Zone (PMIZ) is a mega fisheries industrial project that would retain a large portion of Pacific-caught tuna for local processing. Approved in 2004, it is Papua New Guinea’s (PNG) first project following the Special Economic Zone concept. The project is situated in Bidar, Madang Province and aimed at building ten canneries to create tens of thousands of jobs and generate significant economic activity. The project was estimated to cost US$156 million, funded through a concessional loan from EXIM Bank of China and the Government of PNG. Out of the total land area of 216 ha, 116 ha is allotted for the industrial zone and the remaining 100 ha for residential and commercial use. Upon completion, the PMIZ will have up to ten tuna canneries and a host of integrated port facilities.
Read More
The project is a proposed 180MW hydropower station on the Ramu River. The development is aimed at optimizing the utilization of water resources within the Yonki reservoir to meet increasing load demands and displace high-cost diesel generation. Expected to increase Papua New Guinea’s electricity capacity by 36 percent, Ramu 2 is located downstream of the existing Yonki hydroelectric complex in the Eastern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. The Yonki complex currently consists of two hydro facilities fed from the Yonki dam and reservoir: the 75MW Ramu 1 power station and the 18MW Yonki Toe of Dam hydropower station. The Ramu 2 project will develop the final 570 m head of water in the Ramu gorge between Ramu 1 tailrace Tunnel and the Ramu valley.
Read More
As of September 2021, DITO Telecommunity is the third (and newest) telco operator in the Philippines, breaking the ‘duopoly’ of Globe and Philippines Long Distance Telephone Company (PLDT). San Miguel Corporation, one of the largest corporations in the Philippines, was initially interested in partnering with Telstra Corp., Ltd. to become the third telco, but negotiations fell through. DITO aims to improve the Philippines’ connectivity with faster and more secure high value 4G and 5G technologies.
Read More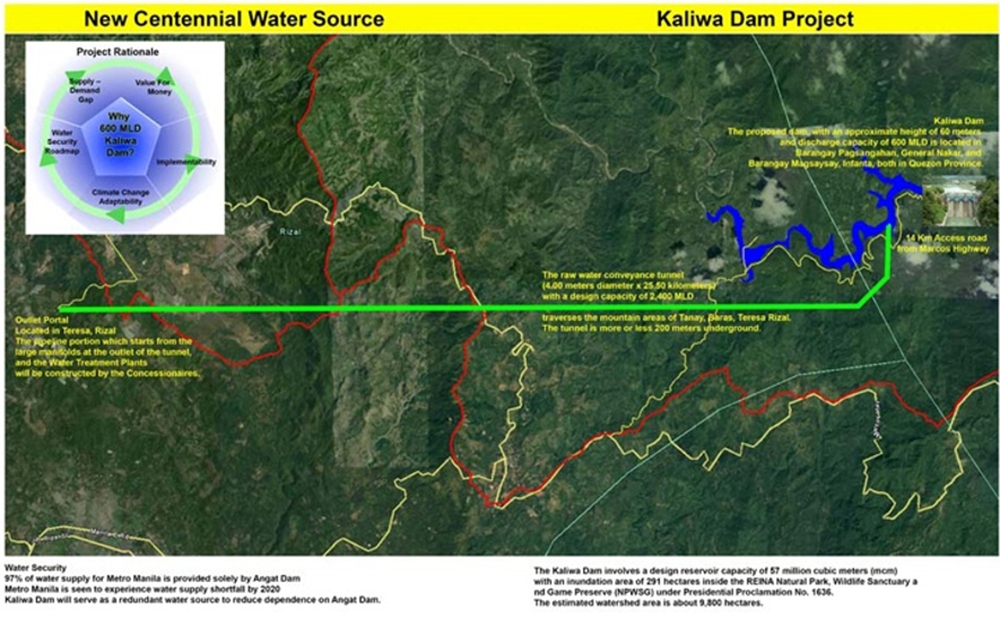
The New Centennial Water Source-Kaliwa Dam Project (NCWS-KDP) is listed as a banner project under the “Build, Build, Build” (BBB) program. It aims to supply 600 million liters of water per day and benefit some 17.46 million people or about 3.49 million households in Metro Manila, Rizal, and Quezon to reduce the current 97 percent dependence on the Angat Dam. The Angat Dam is located in the municipalities of General Nakar and Infanta in Quezon and Teresa in Rizal.
Read More



